What happens if you have liver disease?
If the liver disease is severe enough, more tests are done (ultrasound, MRI, CT scan and biopsy) to achieve the most accurate diagnosis and assess the severity, in order that the most appropriate treatment can be offered.
If left untreated, over time continued liver damage from many causes can lead to cirrhosis, and finally to liver failure (a life-threatening condition). However, mild and early liver diseases are mostly irreversible, provided the cause is removed and treatment is given early.
Therefore, it is important that the liver problem is recognized early so that the cause can be identified and removed if possible, and appropriate treatment is started. If these are done, then in most cases the liver health can be improved or restored. You should of course be under proper medical care.
Things to know about fatty liver
Liver can regenerate itself hence does it mean we do not have to take care of it so much? The answer is no, we should not neglect our liver health as it carries out numerous junctions to our body (as mentioned in the previous article).
Fatty liver is one of the most common liver disorders.
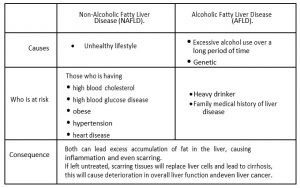
There are 2 types of fatty liver, the first type is Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). According to research from the World Journal Gastroenterology, NAFLD, which is one of the most common liver disorders, affects up to 25% to 30% of the population in the United States and Europe. Another study in Malaysia showed that older people (53-60 years old) have a higher prevalence of NAFLD.
Whereas the second type of fatty liver is Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD). According to statistics in 2010, the prevalence of AFLD is approximately 2% of the United State. People might have a misconception that heavy alcoholic drinkers will have higher risk of liver disease, however looking at the statistics, the fact is NAFLD is more prominent than AFLD.
Table below shows the difference between 2 types of fatty liver
Health and Knowledge:
Some signs and symptoms of fatty Liver are lethargy and abdominal discomfort (mainly on the right side), but mostly are symptomless.
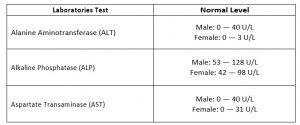
Frequent medical checkup is required to ensure the liver is always in good condition, as most of the fatty liver diseases are found through liver function test and a healthy liver should have enzyme reading as below:
What is the treatment for liver disease?
The treatment for liver disease depends on the diagnosis. Some liver problems can be treated with lifestyle modifications, such as stopping alcohol use or simply losing weight. Other liver problems may be treated with liver tonics, nutritional herbal medications, prescription drugs, or may require surgery. Monitoring of the liver function is done regularly.
If the treatments for severe Liver disease and liver failure fail, the patent may ultimately require a liver transplant.
How to help our liver stay healthy?
- Lead a healthy lifestyle which includes sufficient sleep.
- Healthy diet – avoid red meat, trans-fats, processed carbohydrates and foods with high-fructose corn syrup.
- Exercise 30 to 60 minutes three to four times a week at a moderate intensity.
- Maintain a healthy weight. If overweight or obese — reduce calories and lose weight.
- Avoid or minimize alcohol intake.
- Avoid habitual consumption of paracetamol, other painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. If these are prescribed to you, make sure your doctor monitors your liver function.
There are some nutrients that are essential for liver health, while some spices and herbs can help too. Among the herbal medicines for liver disease that is gaining popularity is the extract of the Taiwanese AC mushroom (Antrodia cinnomomeo, also called AC fungus). It is used in the prevention or treatment of Various diseases of the liver (including hepatitis B), and also kidney disease, food and drug intoxication, diarrhea, abdominal pain, hypertension, itchy skin, and tumors.
Studies have shown promising the treatment of various types hypertension, and alcohol hang over may also help in treating obesity and Laboratory studies show it has ng antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Apart from that, the important nutrients include vitamins A, B (especially B12), D and E; and herbs and spicas include milk thistle, artichoke leaf, turmeric root, dandelion root, yellow dock root, beetroot, radix bupleurum root extract, astragalus membranous root extract and ginger.
Of these, turmeric has gained most attention in the last decade because of its many health benefits, not only for the liver, but for the entire body.
Turmeric has curcuminoids (the most important is curcumin) which have powerful antioxidants and anti-inflammatory actions. These can protect the liver from harmful free radicals, and reduce inflammation brought about by many of the causes of liver damage. Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress (excess free radicals) are the underlying biochemical causes for cellular damage in most other diseases and also in ageing. Turmeric extracts can reduce the risk of fatty liver which affects almost half of us to a certain degree and are especially beneficial for arthritis (as good as using drugs) and other causes of chronic pain.

